Effortlessly deploy large scale distributed Edge infrastructure with Namla’s Zero Touch Deployment

Published on April 01, 2024
Ready for a demo of
Namla
?
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, the deployment of Edge computing devices has become a pivotal strategy for businesses aiming to harness the power of AI and real-time data processing directly at the source of data generation. This trend is particularly visible across various sectors, from retail, with its advanced computer vision for theft detection and self-checkout systems, to the oil and gas industry's push for predictive maintenance on offshore platforms. Such applications not only demand the localized processing capabilities of Edge devices but also underscore the necessity for these systems to be deployed over extensive geographical areas—encompassing hundreds of stores or dozens of offshore platforms spread across continents.
However, the deployment of such vast and complex infrastructures presents extreme challenges. Traditionally, this process has been both time-consuming and expensive, requiring the physical presence of highly skilled technicians to manually set up each device. This not only escalates operational costs significantly but also introduces delays in scaling from proof of concept (PoC) to full production. Moreover, the nature of these deployments entails ongoing maintenance and the periodic replacement of devices, further necessitating on-site technician visits and compounding the logistical challenges.
To address these challenges, Namla developed a complete Zero Touch Deployment (ZTD) solution, that revolutionizes the deployment process by enabling IT teams and system integrators to deploy thousands of Edge devices remotely, without the need for physical on-site interventions. ZTD not only significantly reduces deployment costs and timelines but also minimizes the risk of human errors, thereby facilitating a smoother transition from PoC to production phases. With Namla's Zero Touch Deployment, companies can now leverage the full potential of Edge computing with unprecedented efficiency and scale, transforming the way digital infrastructures are deployed and managed across the globe.
Namla’s Zero Touch Deployment (ZTD) approach
Deploying a distributed edge infrastructure across a country or worldwide requires a high level of expertise. As several solutions claim to provide "Zero Touch Provisioning" (ZTP), although the term's true definition, which describes the management of configurations with no interaction, tends to be misunderstood.
In reality, establishing an infrastructure requires more than a simple zero-touch configuration. Namla has adopted an alternative strategy by building zero-touch deployment (ZTD) into the core of its technology. The ability of setting up and configuring network devices without requiring manual intervention is known as zero-touch deployment. It minimizes the need for on-site technicians, reducing deployment time and lowering the risk of errors.
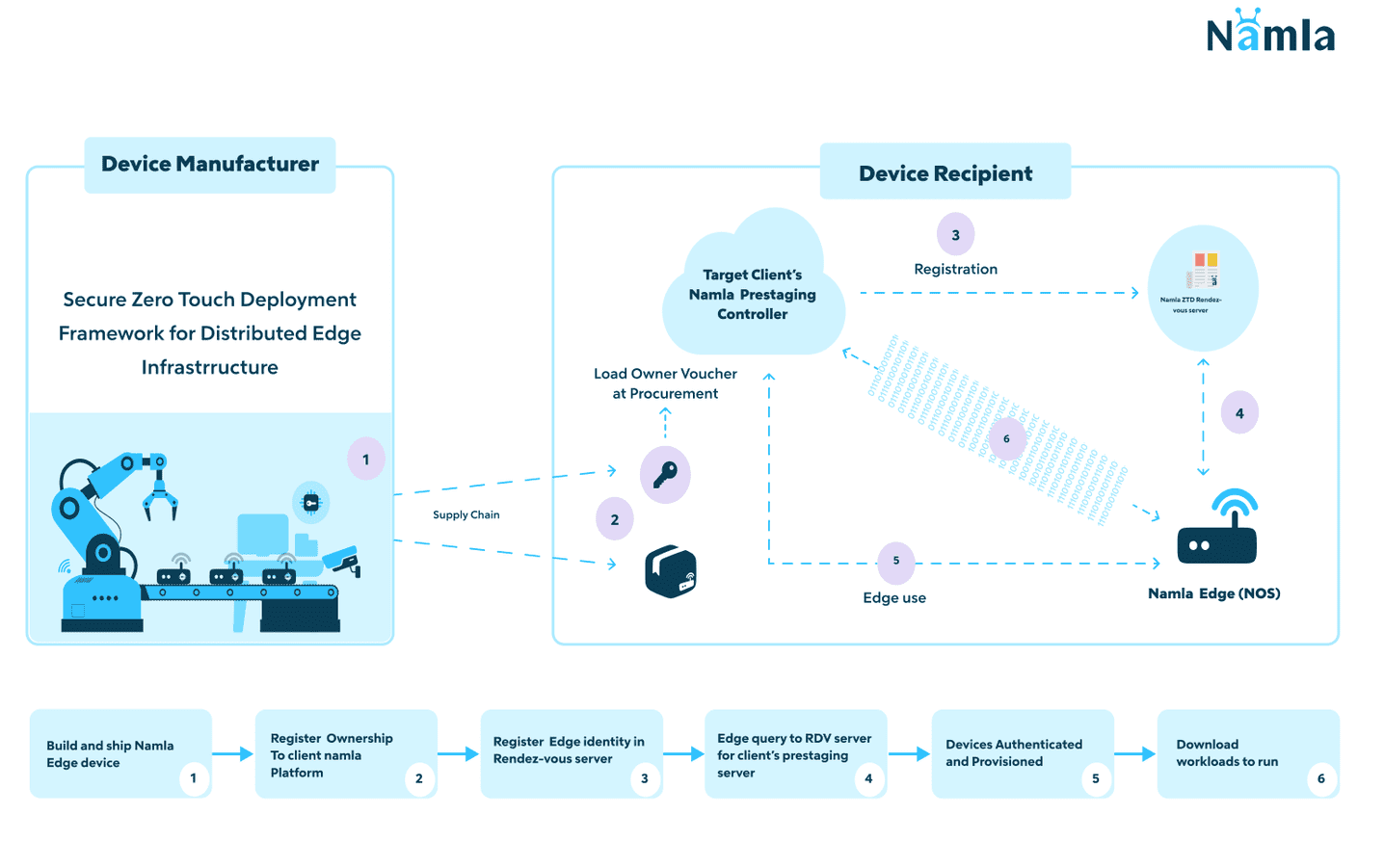
In practice, the process can be summarized in the following steps:
- ● The device is shipped to Edge location and plugged to power and internet (no need for IT skills).
- ● The IT operator remotely registers the device on Namla platform using its serial number.
- ● Once the device is registered onto the platform, its identity is registered into the ZTD Rendez-vous server.
- ● On first boot, the device automatically makes the call to the RDV server to know the client’s prestaging server to use.
- ● The device is then authenticated and provisioning starts automatically.
- ● After 10 to 15 minutes, the Edge is provisioned and workloads can be deployed on it.
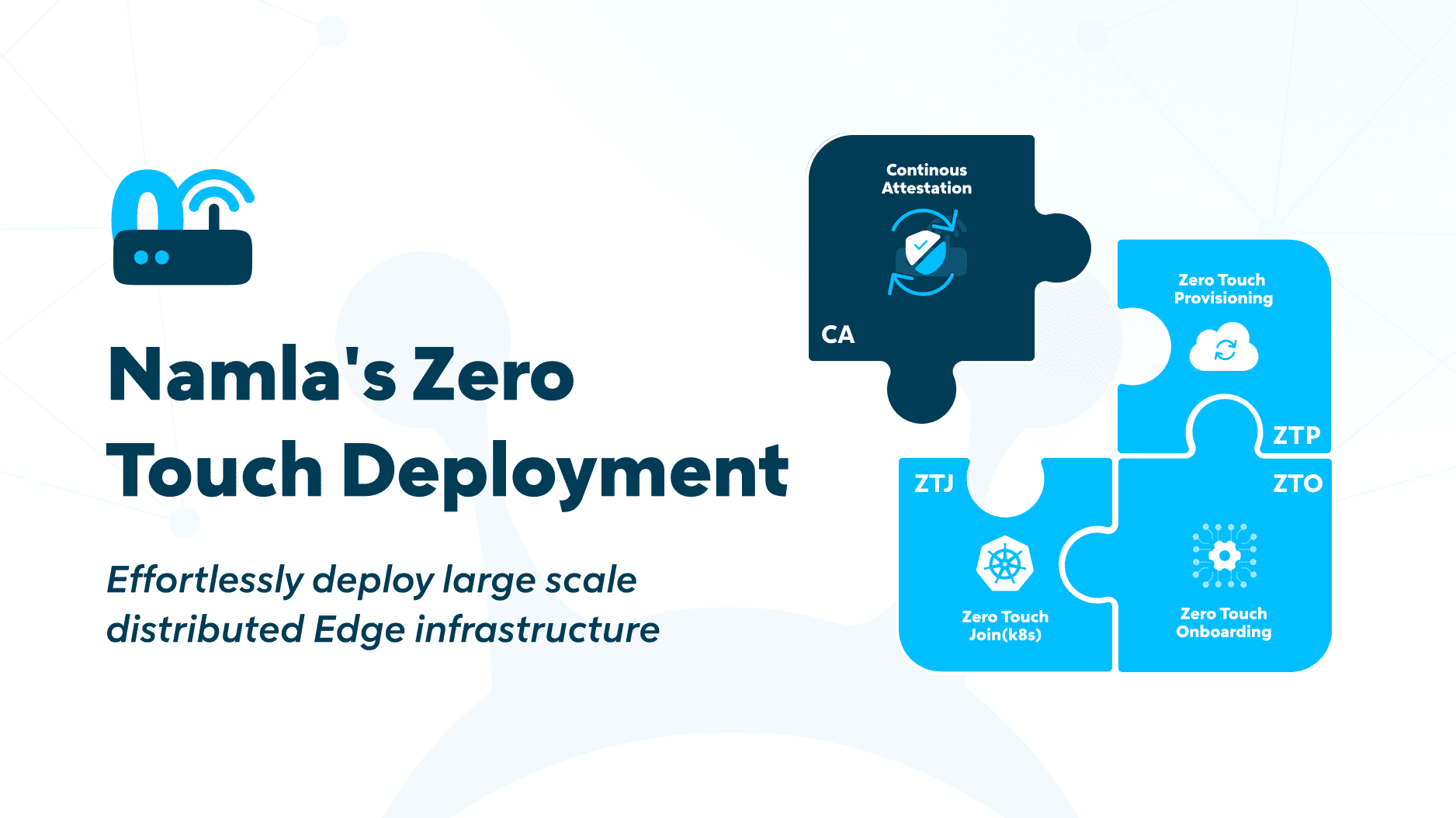
Namla's ZTD process consists of various sub-processes, Zero Touch Onboarding (ZTO), Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP), Zero Touch Join (ZTJ), and includes a security components called Continuous Attestation (CA).
The Power of Zero Touch Onboarding (ZTO) in optimizing Network Device Deployment
Zero Touch Onboarding (ZTO) refers to an automated process that allows device setup and integration into the network by decreasing the necessity for manual intervention. The approach simplifies setups, authentication, and accessibility, boosting productivity and decreasing errors in device onboarding.
ZTO is split into two phases. The verification of the device's identity and ensures that it aligns with the client's profile during the pre-staging procedure. The edge device is linked to the client's approved controllers that were chosen for the specific region during the staging process, which is also known as Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP). Client networking settings and security profiles are applied to the device at this phase.
Zero Touch Joining (ZTJ) streamlines device connectivity
Zero Touch Joining (ZTJ) is an automated method that enables devices to be effortlessly integrated into any system or network with minimal human intervention. ZTJ optimizes the processes needed for devices to connect to the network, ensuring quick and error-free connectivity. This approach improves efficiency, conserves deployment time, and minimizes the probability of human error in the joining procedure.
The device is authorized to associate with the client’s digital cluster in the Zero Touch Joining phase, which constitutes the final stage in Namla’s Zero Touch Deployment procedure. The edge device is now operational and ready to perform client workloads such as Kubernetes defaults.
Improving Network Security and Compliance Via Continuous Attestation (CA)
Namla introduces Continuous Attestation (CA) into its ZTD process, which is an essential preventative measure employed to guarantee the reliability and safety of devices and systems. It operates by autonomously and consistently examining multiple features of a device, including its boot process, configuration, and identity. This continuing assessment ensures that the device retains its integrity and complies with established safety standards throughout time, which is particularly crucial in dynamic and evolving contexts.
Namla provides continuous attestation methods for preserving the security of edge devices in their physical surroundings. This requires regular safety evaluations, including an examination of the device's boot sequence. Namla's controllers provide the essential function of keeping the device's identity.
Namla's innovative Zero Touch Deployment represents a transformative shift in the deployment of edge infrastructure, offering IT teams and system integrators a streamlined, remote deployment process for thousands of devices. This not only accelerates the time to market for Edge Computing projects, but significantly reduces associated costs by eliminating the need for onsite visits.
This groundbreaking method removes the necessity for time-consuming manual settings, bringing in a new era of greater efficiency and accuracy. While the promise of zero-touch provisioning emerges as a sign for enabling the global deployment of distributed edge infrastructure, Namla's entire technique elevates this concept to new heights.